Which soil is suitable for agriculture

The question that always comes to the mind of every farmer or future farmer is Which soil is suitable for agriculture. Every expert’s opinion is different.
Basically, so far, no soil has been created or prepared that will sustain all crops. Each soil has a history, a feature, different properties, different compositions, and each has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Apart from paying attention to which is the best soil. It should be which crops are good for your soil and how to improve our soil quality.
What Is Soil in Agriculture?
The definition of soil in agriculture is soil that contains nutrients substant, minerals, water absorption quality, and organic matters that helps to grow plants and crops.
The quality of soils or Parameters of each substance in soils is varied as per their geographic and soils formation conditions. And that is the only reason there is no single type of soil suitable for all crops.
Every soil in agriculture has different specifications and characteristics. Some soils are dry, hot, or sandy in nature, so they need more water, and some soils are good at moisturizing, so they consume less percentage of water. Hard soil needs more rotors and tillers than other soils. Some soils need more manure or fertilizer, and some need less than others.
We will discuss all these parameters in the details in types of soils, but before that, we will take a quick overview of “what is soil organic matter?.”
What is Soil Organic Matter?
Soil organic matter is one of the finest components in agricultural soil. Soil organic matter is a fraction of soil which consist of many composts, living thing, manure, biomass, plant, and animal tissue.
It helped in the growth of crops and gave strength to fight against Insects and germs.
In every agricultural land, 3% to 6% of soil organic matters are present. That means the health of your agricultural land is good. If you are not aware of how much percent of soil organic matter is present in your soil then, I suggest you do a soil test.
And if your land has less soil organic matter, then add more amount of compost and manure.
Which Soil is Suitable for Agriculture
As before I said, every soil has its own structure, composition, properties, and specialty. So the argument on which soil is best for agriculture is not right. Instead of that, we have to think about which crops are suitable for our soil type.
Each soil is made for a specific crop. To increase your productivity, you need to know which crop is suitable for your land. And we should focus on how we can increase its quality and quantity.
Types of soil
If you make your mind to be a farmer, you must have to check the type of soil of your farm.
There are several types of soils that vary from region to region and fertility. So, we will see Characteristics, Nutrients, the region or area where soils are found according to India, and which crops are best.
1. Black Soil or Black cotton soil
Black soil is also known as regur soil, cotton soil, or black cotton soil.
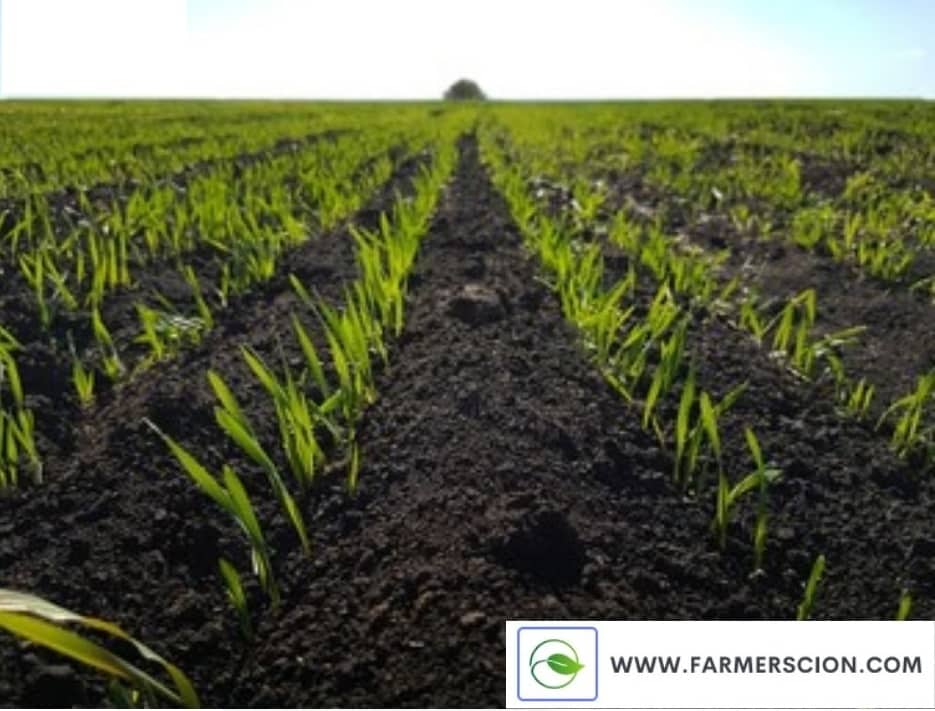

Formation of back soil
The overflowed lava from the volcano cools and turns into black rock, and the overtime air turns the rock into soil. That is why this soil is also called regur soil and lava soil.
Nutrient in Black Soil
Black soils have contained a huge amount of calcium, potassium, and magnesium but are low in nitrogen.
Crops grown in black soil
The best crops are grown in black soils are cotton, tobacco, millets, fruits (majorly citrus fruits). besides all these crops, black soil is also suitable for maize, sunflower, castor, oilseeds, Jowar, millets, linseed, tobacco, safflower, sugar cane, vegetables.
Advantage of black soil cotton soil
- best and highly used for agriculture
- required less amount of fertilizer and manure.
- Balance in nutrients and minerals (calcium carbonate, magnesium, potash, and lime)
- Require less water for irrigation
- max numbers of crops are taken.
Disadvantage of black soil
- poor in nitrogen and zinc
- Water management is necessary. (black soil is good in consuming water and well in moisturizing, but it’s hard to maintain if you provide a high amount of water. In another circumstance, it’s crack if soil dry )
- Hard to cultivate and tillage in wet and dry black soil.
2. Alluvial Soils
Alluvial soil is one of the precious and important soils for agriculture. Alluvial soil is the finest soil for fertile soils for cultivation.
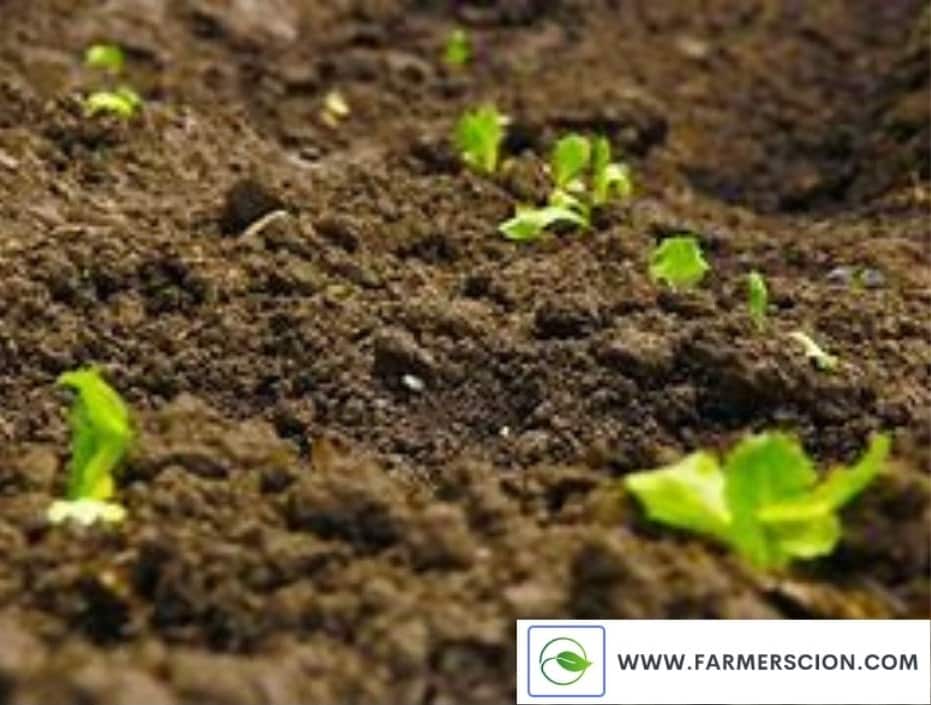

Formation of Alluvial Soil
Alluvial soil is deposited by Surface-water. It is found around rivers, floodplains and deltas.
Floods characterize alluvial soils. Because floods deposit fresh organic silt to the surface frequently, that’s why alluvial soils have a distinct layered appearance.
Nutrient in Alluvial Soil
Alluvial soil is rich in minerals and nutrients, making it a particularly fruitful agricultural soil. It is frequently composed of gravel, sand, and silt.
Crops grown in alluvial soil
Alluvial soils are said to be the finest for agriculture. They tolerate a variety of irrigation methods, including well and tube-well systems. They are beneficial to a wide range of crops, including rice, wheat, sugarcane, tobacco, maize, oilseeds, vegetables, and fruits.
Advantage of allivial soil
- Alluvial soil is most fertile soil.
- Alluvial soil also give best responce to canal and tubewell.
- Max number of nutrients are presents.
- Alluvial high water retention capacity.
Disadvantage of Alluvial Soil
- Old alluvial soil is not fit for further cultivation as it loses its fertility.
- Construction work cannot be carried out
3. Red and Yellow Soil
Red soil has low water consumption capacity even though it’s good or used for agriculture. Red soil is mostly found in South America, Central Africa, South and Southeast Asia, China, India, Japan, and Australian countries.

Formation of Red Soil
Weathering of ancient old crystalline igneous and metamorphic rocks, mainly acid granites and gneisses, quartzitic rocks, and felspathic rocks, produces it. It has high iron content and hence appears red. Red soil is also known as yellow soil.
Nutrient in Red Soil
Red soil contains a large amount of non-soluble material, potash, iron, aluminum, and organic matter.
Red soil contains less magnesium, phosphoric acid, lime, nitrogen, humus, carbon dioxide, and soda.
Crops grown in red soil
Best crops grown in red soil are wheat, cotton, tobacco, root crops (potatoes, ginger), pulses, jowar, linseed, millet and fruits.
Advantage of red soil
- Iron, potash, organic matter, and aluminum levels are all greater in red soils.
- In comparison to other soils, red soil has a higher drainage capacity, and it is porous, fine-grained, and fertile.
Disadvantage of red Soil
- The acidity of red soil is high.
- The red soil is thin, porous, and littered with loose pebbles.
- It also has low levels of lime, phosphate, nitrogen, and humus.
4. Sandy Soil
Particles in sandy soil are big and hence a lot of air is trapped within them. Because of that sandy soil is light in weight and dry in nature. These soils drain quickly or the big soil of sandy soil can not retain the water. They warm up faster in the spring than clay soils, but they dry up in the summer and suffer from poor nutrients that are washed away.
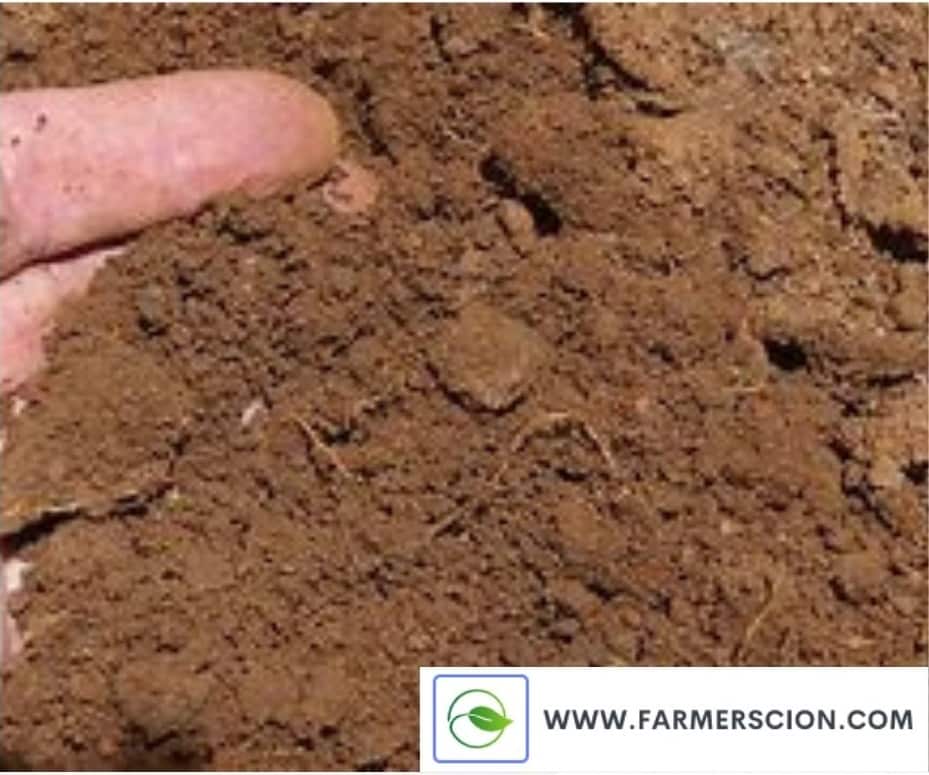

Formation of Sandy soil
In sandy soils, podzolization can be seen after only a hundred years of soil formation; however, the development of mature podzols can take anywhere from more than 5 000 years.
Nutrient in sandy soil
Sandy soil contains the acidic element, it is holding phosphate for more time than nitrogen potash and calcium.
Crops grown in sandy soil
Suitable crops for sandy soils are coconuts, cucumber, sweetcorns, tomatoes, pole beans, peppers, green beans, Carrots, Radishes, Potatoes, Lettuce, Collard greens, Zucchini, Watermelon.
Advantage of Sandy soil
- In general, sandy soils drain well and hold little water.
- Because sandy soils are frequently acidic, acid-loving plants thrive.
- They are dry and warm in the spring, allowing for early sowing and planting, and they yield excellent early vegetable harvests.
- Some sandy soils include fine sand.
- Sand is light and easy to dig, and it may be grown all year.
Disadvantage of Sandy Soil
- Dry quickly.
- Less water consumption quality.
- fewer nutrients are contained.
5. Peaty Soil
The top layer surface of peat soil is rich in organic matter. Most organic matter is obtained from plants or dead organic matter.
Peat soil carries around 60% of organic matter. Peat soil takes more time you warm up itself. Peat soil is best for fertile but waterlogging, high acidity, oxygen deficiency, low bearing capacity, nutrient deficiency are the main issue.
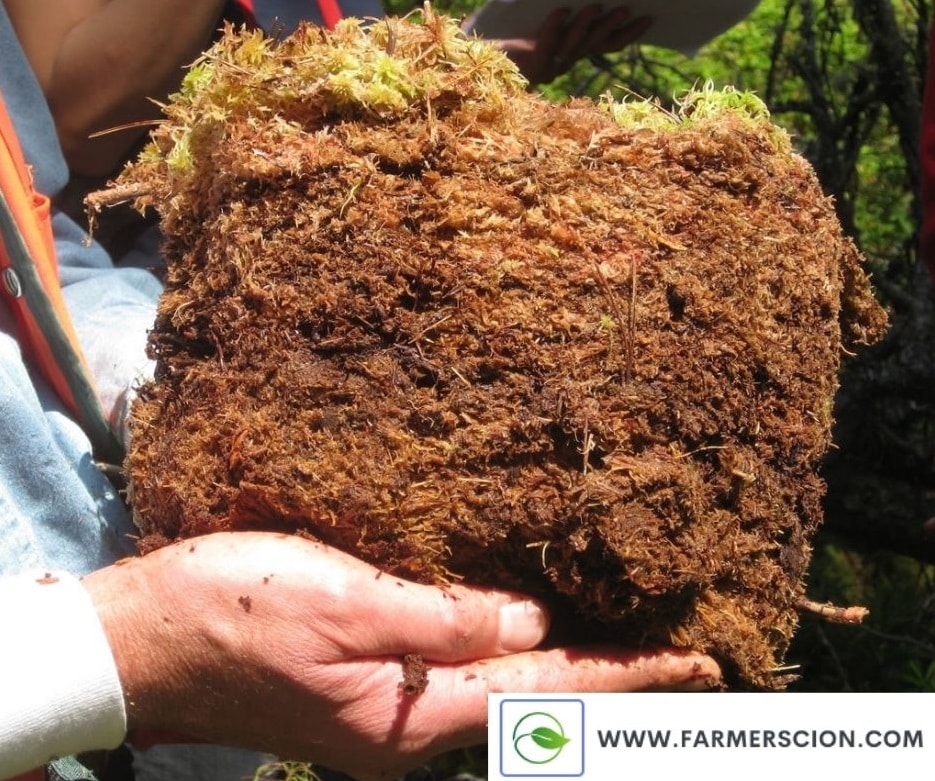

Formation of Peat Soil.
They are found in areas of heavy rainfall and high humidity. Peat soils are found in all regions but are more widespread in the temperate and cold zones of the Northern Hemisphere.
Nutrient in Peat Soil
Magnesium, Phosphorus, Nitrogen, calcium, and potassium are all incorporated in peat soil and play significant roles in plant development, refuse breakdown, and the biogeochemical functioning of peatlands.
Crops Grown in Peat Soil
Peat soil is one of the finest soil for fertile and with well amount of organic matter. In peat soil, we can grow fruits, vegetables and crops like cabbage, Cauliflower, legumes, carrots, Heather (flowers), Lantern Trees, Camellia, sugar beet, potatoes, celery, onions, lettuce.
Advantages of Peat Soil
- Abundant in organic matter.
- High quantity production.
- Good at fertile and moisturization.
- Near around 60% of organic matter.
Disadvantages of peat soil
- Water logging is the major problem of peat soil.
- organic matter overflowed while raining,
- Oxygen and nutrient deficiency.
- High in acidity
6. Clay Soil
Clay soil is made up of very tiny mineral particles and little organic material. Because there isn’t much space between the mineral particles, the resulting soil is extremely sticky. These soils are made up of more than 25% clay, and because of the gaps found between clay particles, clay soils store a lot of water.

Formation of Clay Soil
Weathering can alter pre-existing minerals to form clay and clay-based minerals. Clay minerals most commonly form by prolonged chemical weathering of silicate-bearing rocks. Chemical weathering takes place largely by acid hydrolysis due to low concentrations of carbonic acid, dissolved in rainwater or released by plant roots.
Nutrients in Clay Soil
Clay Soil Contains a Well Amount of Calcium, Potassium, and Magnesium.
Crops Grown in Clay Soil
Clay Soil’s Capacity to Retain Moisture Benefits Lettuce, Chard, Snap Beans, and Other Crops with Shallow Roots, While Broccoli, Brussels Sprouts, and Cabbage Frequently Grow Better in Clay Soil Than Looser Loams Because Their Roots Have Strong Anchoring.
Advantage of Clay Soil
- Compacted Clay Prevents Grass and Other Plants from Growing Properly.
- Organic Matter and Gypsum Are Soil Additives That Enhance Heavy Clay and Reduce Compaction.
- Gypsum Improves Your Soil and Provides Additional Advantages to Your Plants.
Disadvantage of Clay Soil
- Poor Drainage, Particularly When Compacted.
2. It’s Difficult to Dig, and It Warms Up Slowly.
7. Silt Soil
Silty Soils Are Often Well-Aggregated. When Wetted, the Aggregates Break Down Quickly, Allowing Nonaggregated Soil Particles to Be Easily Transported.
Silty Soil Is Neither Grainy nor Rocky, but Rocks Such as Siltstone Develop When Silt Deposits Are Crushed and the Grains Are Pushed Together. Silt Is Formed When Water and Ice Erode or Wear Away Rock.

Formation of Slit Soil
Silt Is Formed When Water and Ice Erode or Wear Away Rock. as Small Rock Fragments Are Transported by Rushing Water, They Scrape Against the Sides and Bottoms of Stream Banks, Chipping Away Additional Rock. the Particles Collide and Grind Against One Other, Growing Smaller and Smaller Until They Are Silt-Sized.
Nutrient in Silt Soil
the Mud Particles Are Large Enough to Drain Well but Small Enough to Contain More Plant Nutrients Than Sand.
Crops Grown in Silt Soil
Mainly Fruits, Grass Are Taken. Root Vegetables Are Also Grown in Silty Soil
Advantage of Silt Soil
- Silty Soils Are Usually More Fertile Than Other Types of Soils.
- It Is Good for Cultivating
- Sludge Increases Water Retention and Air Circulation.
Disadvantages of Silt Soil
- Can Be Compact and Hard
- Water Filtration Can Be Bad.
8. Loam Soil
Loam Soil with a Mixed Composition of Sand, Silt, and Clay. This Soil Is Among the Best Well-Drained Soils. There Are Two Types of Loam Soil, Clay-Loam or Sandy-Loam, Depending Upon the Percentage Composition of Components.

Formation of Loam Soil
Loam Soil Is a Combination of Three Different Types of Soil—sand, Silt, and Clay—each with Its Own Characteristics.
Nutrient of Loam Soil
Loam Soils Generally Have More Nutrients, Moisture and Humus Than Sandy Soils, Have Better Drainage and Infiltration of Water and Air Than Soils with Silt and Clay, and Are Easier Than Clay Soils.
Crops Grown in Loam Soil
We Can Grow Wheat, Sugarcane, Pulses, Peppers, Green Beans, Oilseeds, Cotton, Tomatoes, Cucumber, Onions and Lettuce in the Loam Soil.
Advantage of Loam Soil
- Loam Soil Is an Optimal Combination of the Three Since It Stores Water.
- Loamy Soils Have a High Tilth and Are Loose and Crumbly Rather Than Sticky and Compacted.
- When Properly Cared For, Holds Nutrients Better Than Other Soil Types.
- It Warms Up Faster in the Spring Than Clay.
Disadvantages of Loamy Soils
- Depending on How Your Soil Was Produced, Certain Loamy Soils May Include Stones That Might Interfere with Crop Harvesting.
- Extremely Prone to Compaction
- When Wet, It Is Sticky and Difficult to Work With, and When Dry, It Is Prone to Breaking.
- Can Be Prone to Waterlogging, Preventing Grass from Obtaining Adequate Air.
9. Desert Soil
The Desert Soil Is Dry, It Has Very Little Moisture, and It Has Very Little Organic Matter. They Change Greatly in Texture; Most Are Sandy and Gravelly, While Some Have Layers of Sticky Clay or Even Rocky Layers of White Lime.

Formation of Desert Soil
The lack of rain Has Created Desert Soils, Also Known as Arid Climates. The Desert Soil Is Mainly Sandy Soil (90-95%).
Nutrient in Desert Soil
It Is Rich in Calcium, Carbonate and Phosphate and Low in Nitrogen and Organic Matter.
Crops Grown in Desert Soil
Desert Useful to Grow Crops Such as Barley, Rape, Cotton, Wheat, Millets, Maize, Pulses, Bajra, Wheat, Small Grains, Watermelons, Cherries, Tomatoes, Cucumber.
Advantage of Desert Soil
- Rich in Nutrients ( Because of Less Rainfall, Nutrients Are Not Washout)
- It Contains a Very Low Salt Concentration.
- It’s Good for Growing Plants.
- Well, Amounts of Organic Matter Are Present.
Disadvantages of Desert Soil
- Fertilization Is Hard in Desert Soil.
- Less Water Contains.
- Weather Change Dramatically.
- Need More Soil Management.